
Supported arguments are type ( "norm", "basic", "stud", "perc", "bca"), parallel and the number of bootstrap replicates R. Defaults to FALSE.įurther arguments are passed to the boot function. Logical, indicating whether NA values should be stripped before the computation proceeds. "left" would be analogue to a hypothesis of "greater" in a t.test. Default is NA.Ī character string specifying the side of the confidence interval, must be one of "two.sided" (default), "left" or "right". The value should be any subset of the values "classic", "boot".Ĭonfidence level of the interval. An object which is not a vector is coerced (if possible) by as.vector.Ī vector of character strings representing the type of intervals required. Sides = c("two.sided","left","right"), na.rm = FALSE. Usage Gmean(x, method = c("classic", "boot"), conf.level = NA,
AndersonDarlingTest: Anderson-Darling Test of Goodness-of-Fit.AllIdentical: Test Multiple Objects for Exact Equality.AllDuplicated: Index Vector of All Values Involved in Ties.Agree: Raw Simple And Extended Percentage Agreement.

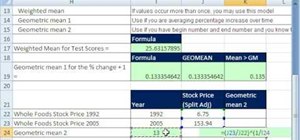
AddMonthsYM: Add a Month to a Date in YearMonth Format.Abstract: Display Compact Abstract of a Data Frame.ABCCoords: Coordinates for "bottomright", etc.If even one point is zero, the mean is zero, which provides little useful information, and if one or more points is negative, even if the mean is possible to calculate, the result would have little relavence to the actual data, since the same result would be obtained if different numbers in the set were negative.įor more information about geometric means, visit our reference unit on Pythagorean Means. The second way is to say that a geometric mean is of no practical value unless all the points are positive. The first way is that if you have an even number of data points, and an odd number of those points is negative, this will result in an even root of a negative number, which is not defined. Under what circumstances will a geometric mean not exist? There are two ways of answering this question. Geometric means are always less than or equal to the arithmetic mean of the same number. ExplanationThe geometric mean is obtained by taking the product of the data points, and then taking the n th root of the product, where n is the number of points in the set. Geometric Mean Please enter data above to calculate the geometric mean.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
